A new study has found that people who work night shifts are at a higher risk of developing kidney stones.
According to foreign media reports, individuals doing desk jobs during night shifts have a 15% to 22% greater risk of kidney stone formation.
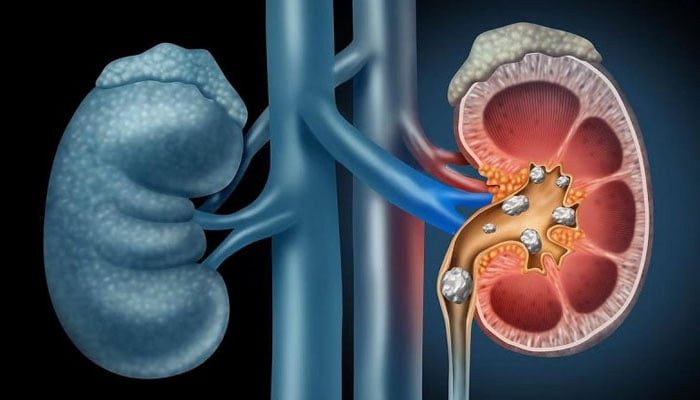
The UK’s National Kidney Foundation states that kidney stones are hard deposits formed inside the organs from chemicals present in urine. These stones can cause pain while passing through the urinary tract.
Dr. Felix Knauf, a nephrologist at Mayo Clinic in Rochester, Minnesota, said that kidney stones can be silent or may cause severe complications especially intense pain that may require hospitalization.
For this new research, scientists analyzed data from over 220,000 participants in the UK Biobank Health Study. During an average follow-up of about 14 years, nearly 2,900 participants developed kidney stones.
The study revealed that individuals who worked shifts other than the regular 9-to-5 schedule had a 15% higher risk of kidney stones. Those who often or always worked such shifts faced a 19% higher risk compared to those who did not work night shifts.
Researchers pointed out that smoking, poor sleep, lack of physical activity, higher body mass index (BMI), and inadequate water intake are all factors that increase the likelihood of kidney stone formation.
According to Dr. Knauf, the disruption of a person’s sleep-wake cycle known as the circadian rhythm caused by shift work also contributes to the risk, as it affects the body’s water balance and biochemical regulation systems.
Professor Young stated that to improve the health of shift workers, controlling weight, drinking plenty of water, getting good sleep, reducing sedentary work, and quitting smoking are effective measures. These steps can reduce the negative impacts of shift work and lower the risk of kidney stones. By adopting a healthier lifestyle, shift workers can make a meaningful improvement in their urological health.